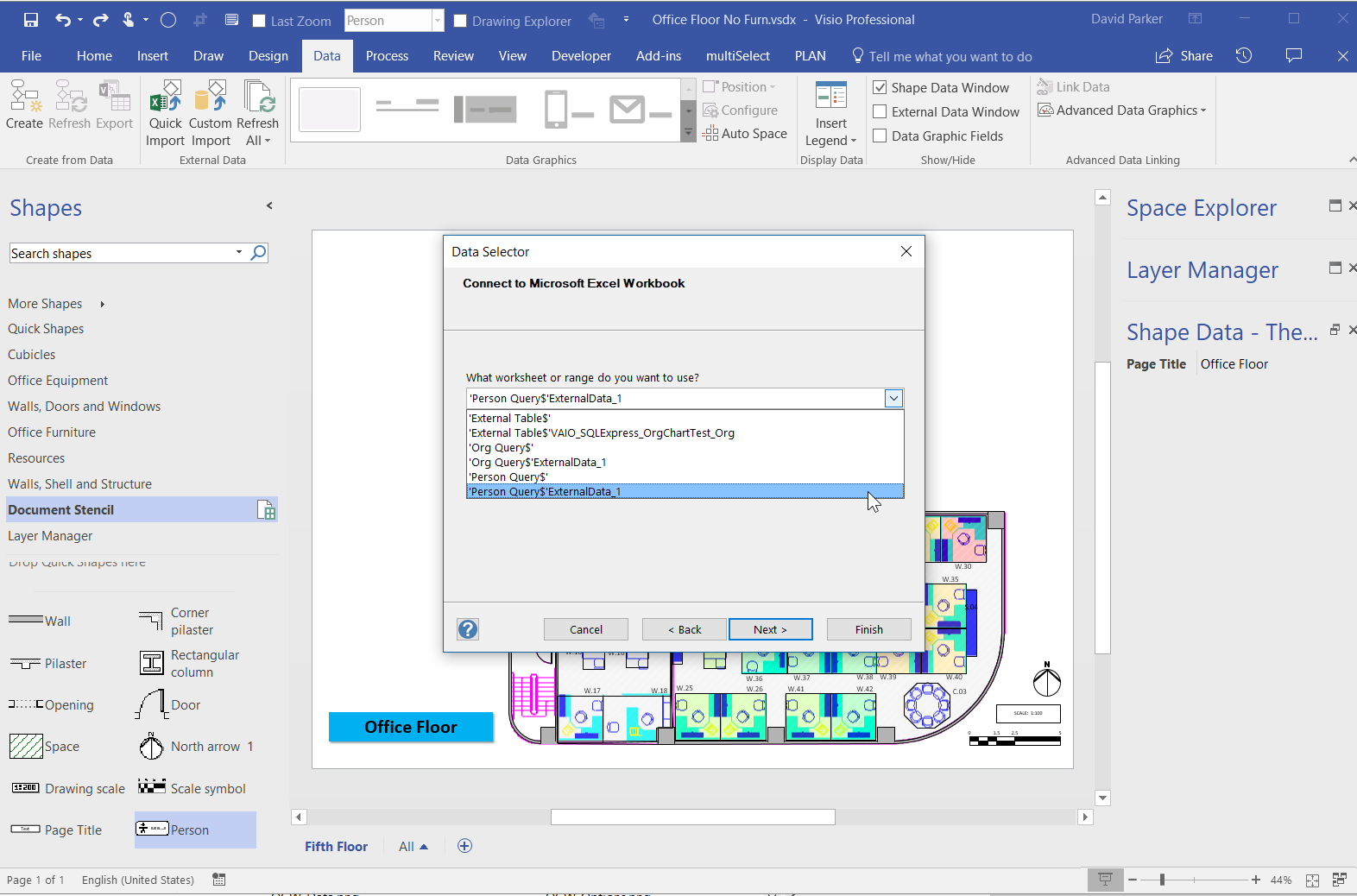
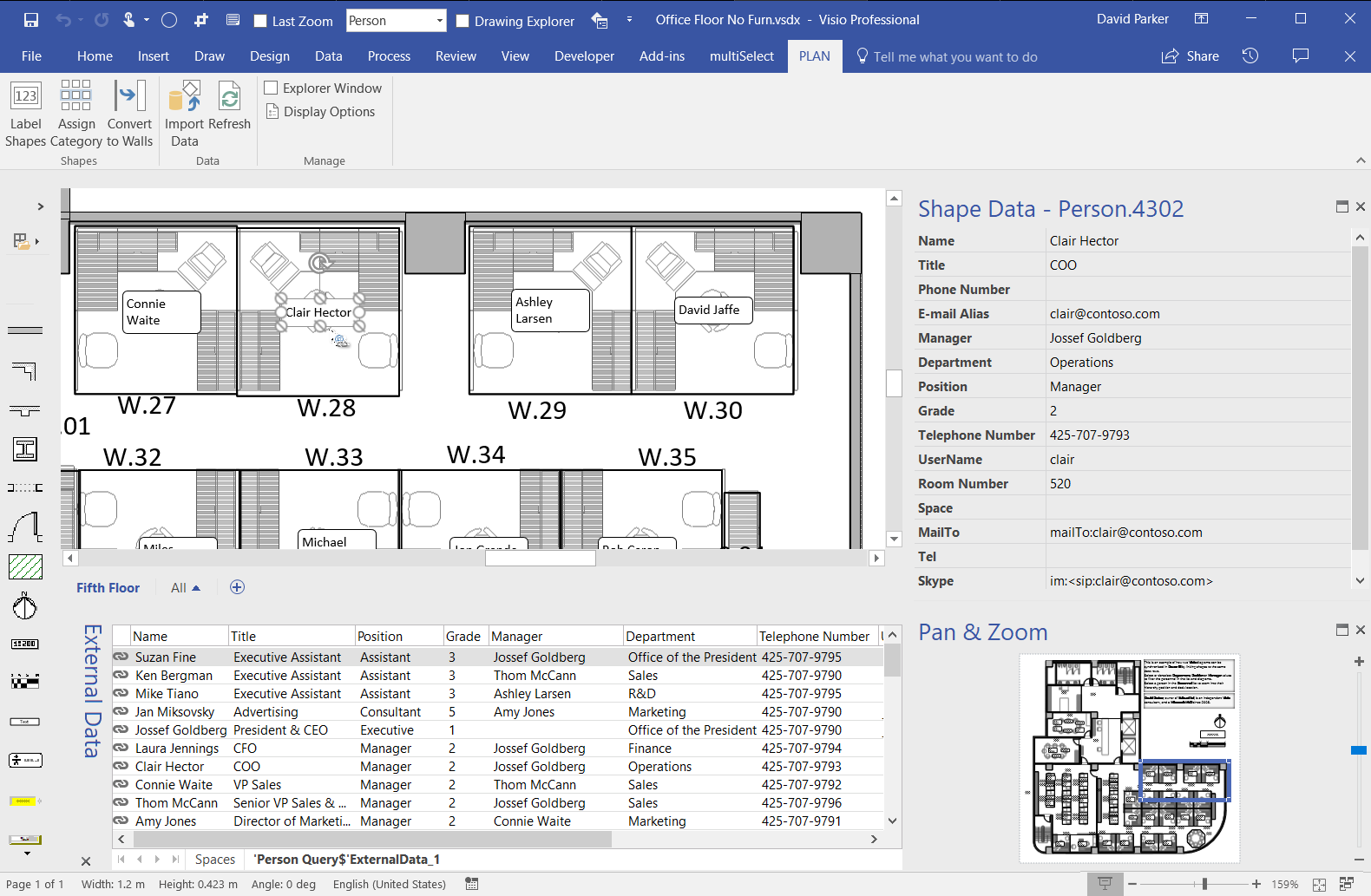
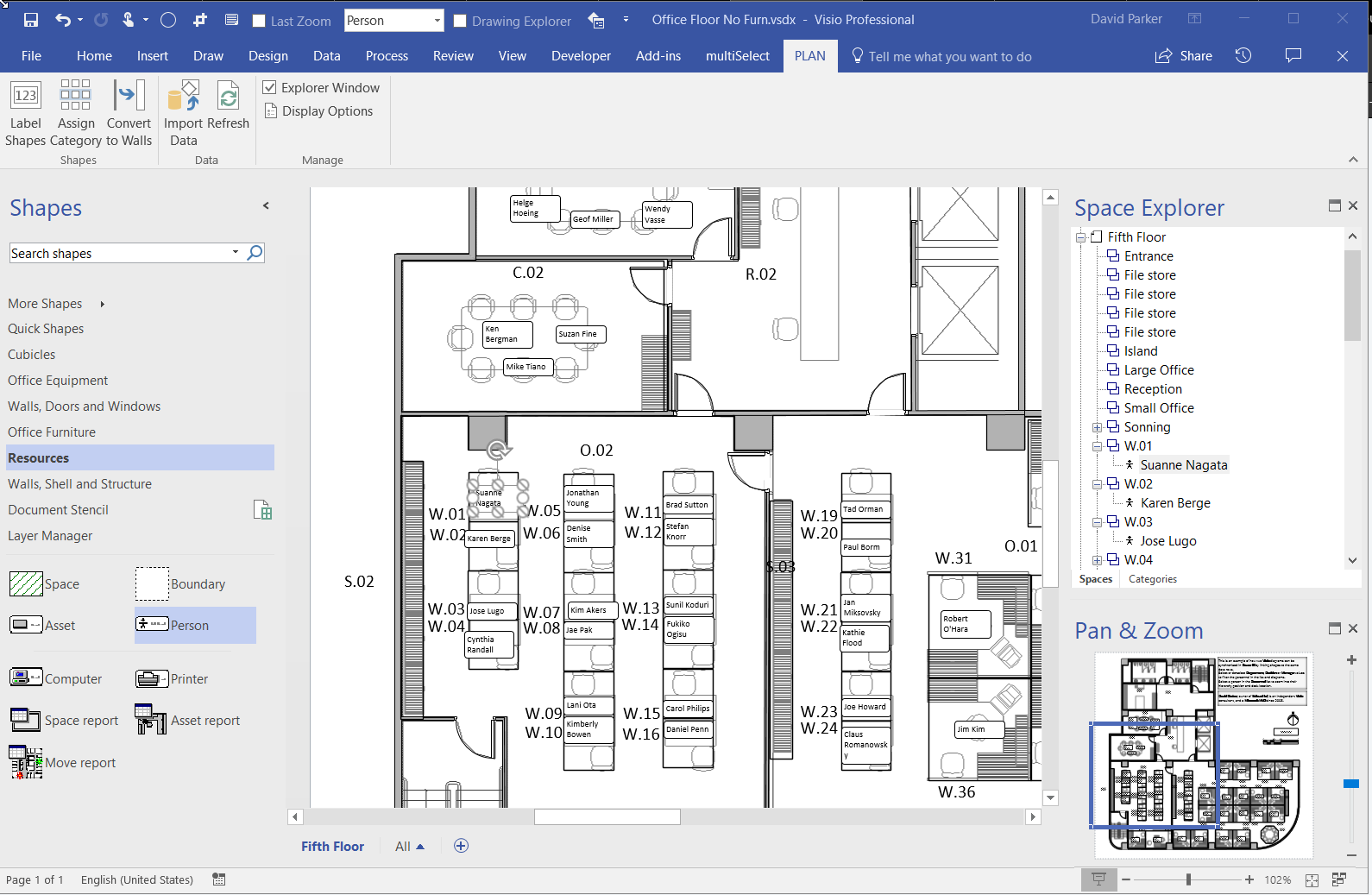
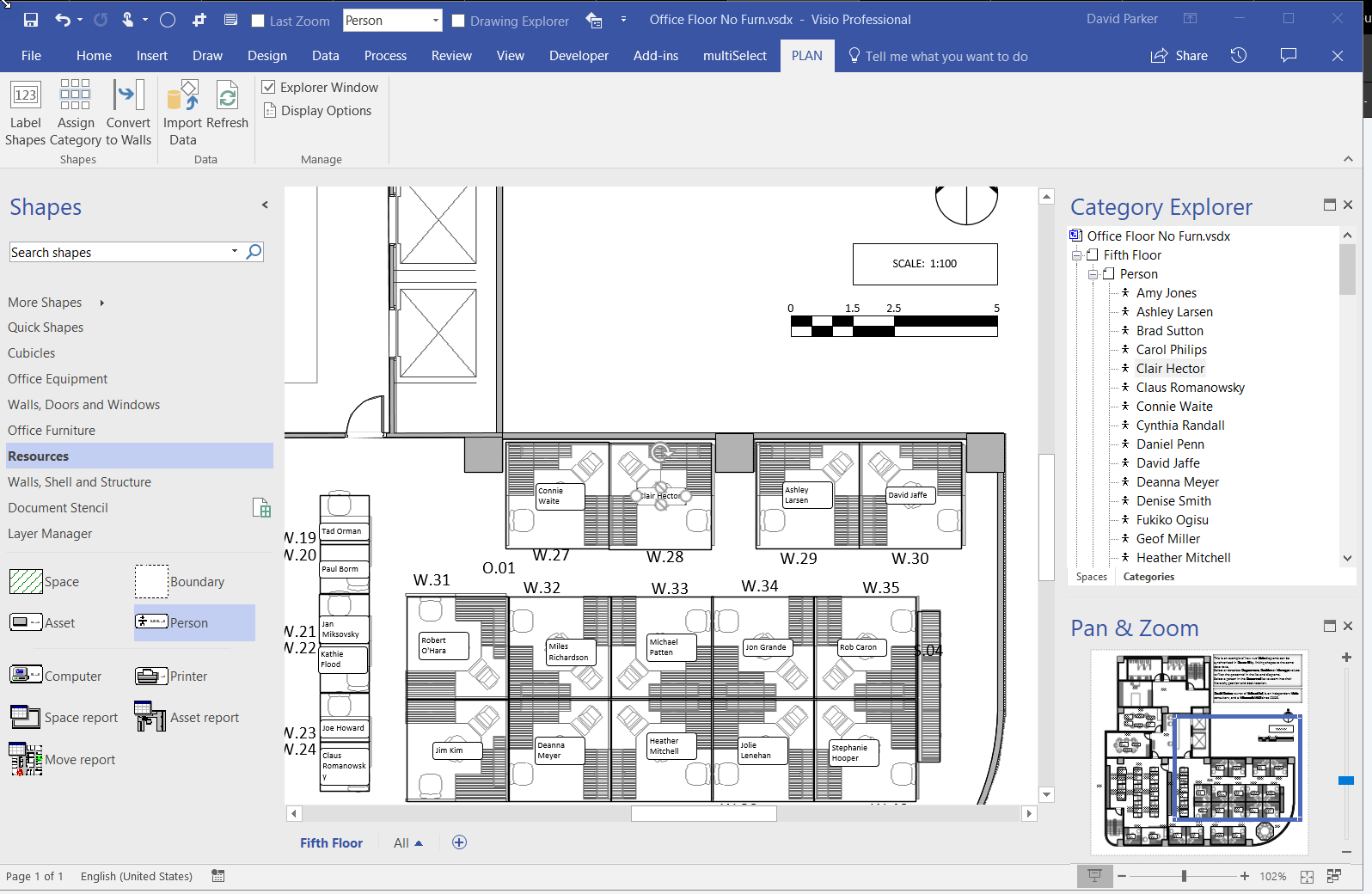
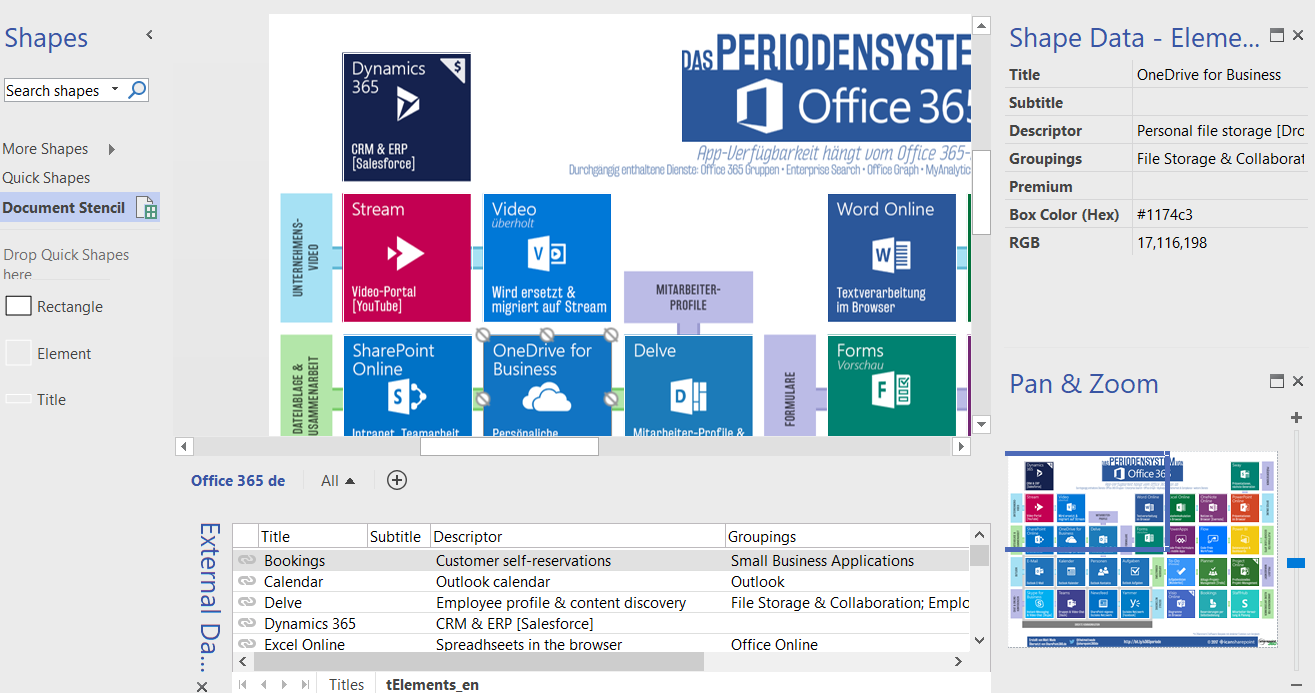
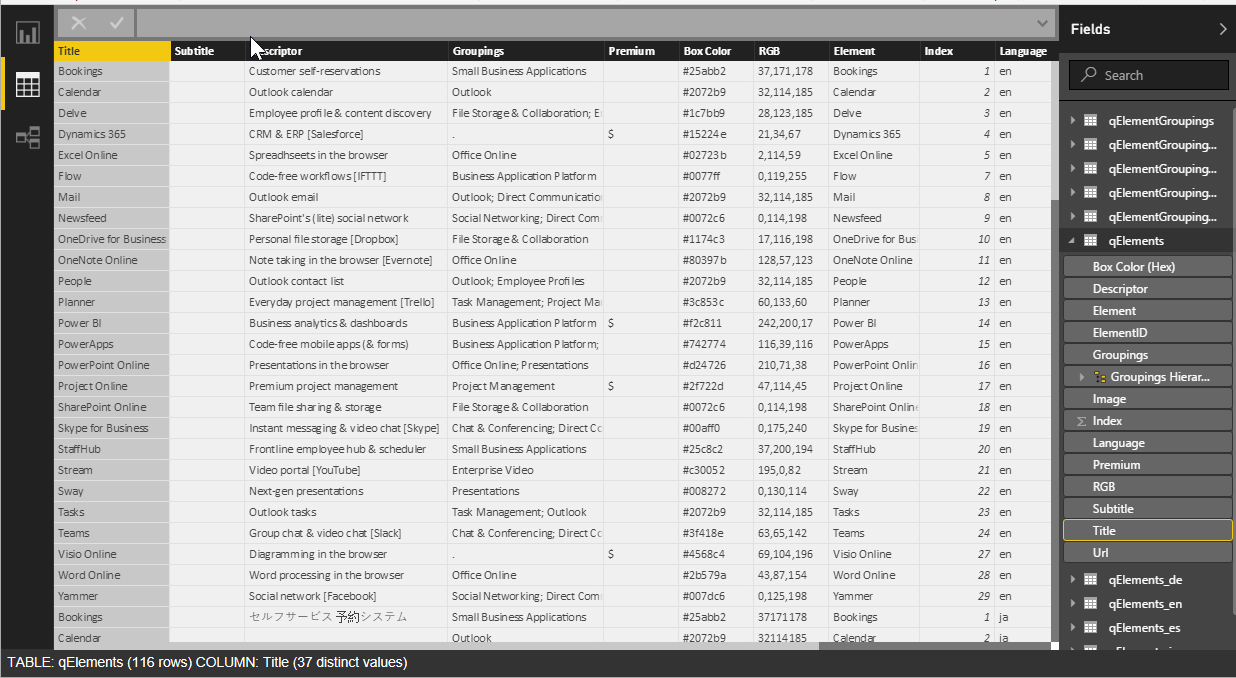
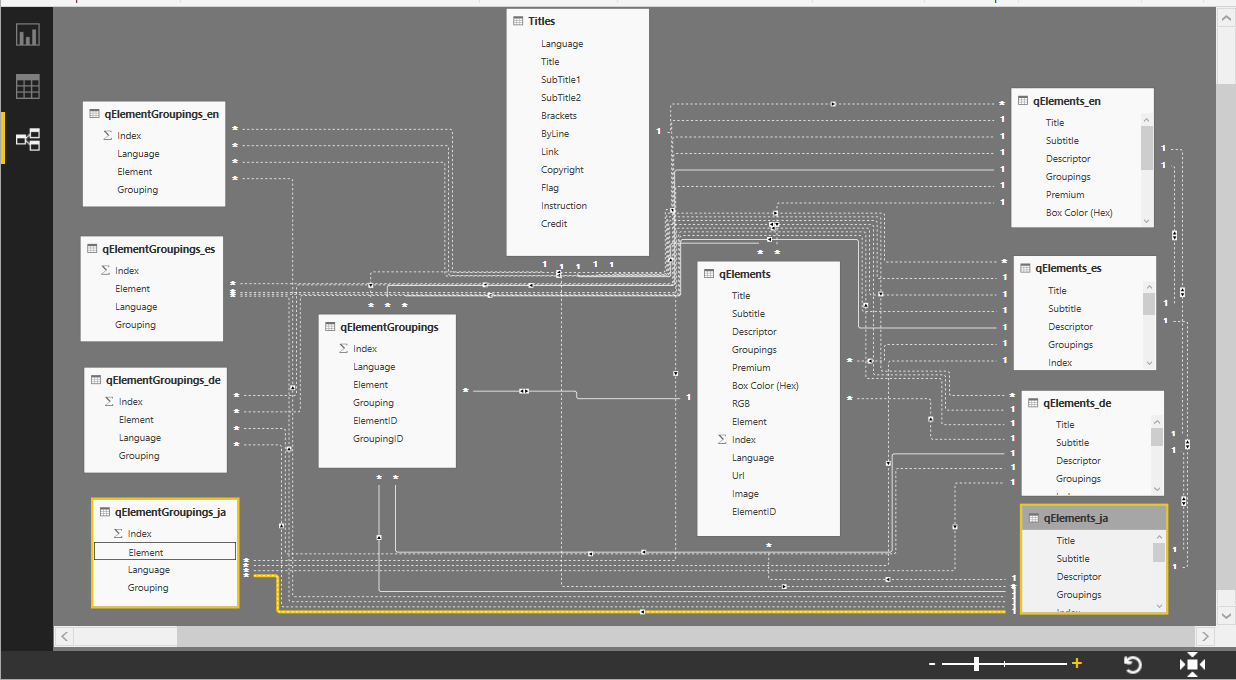
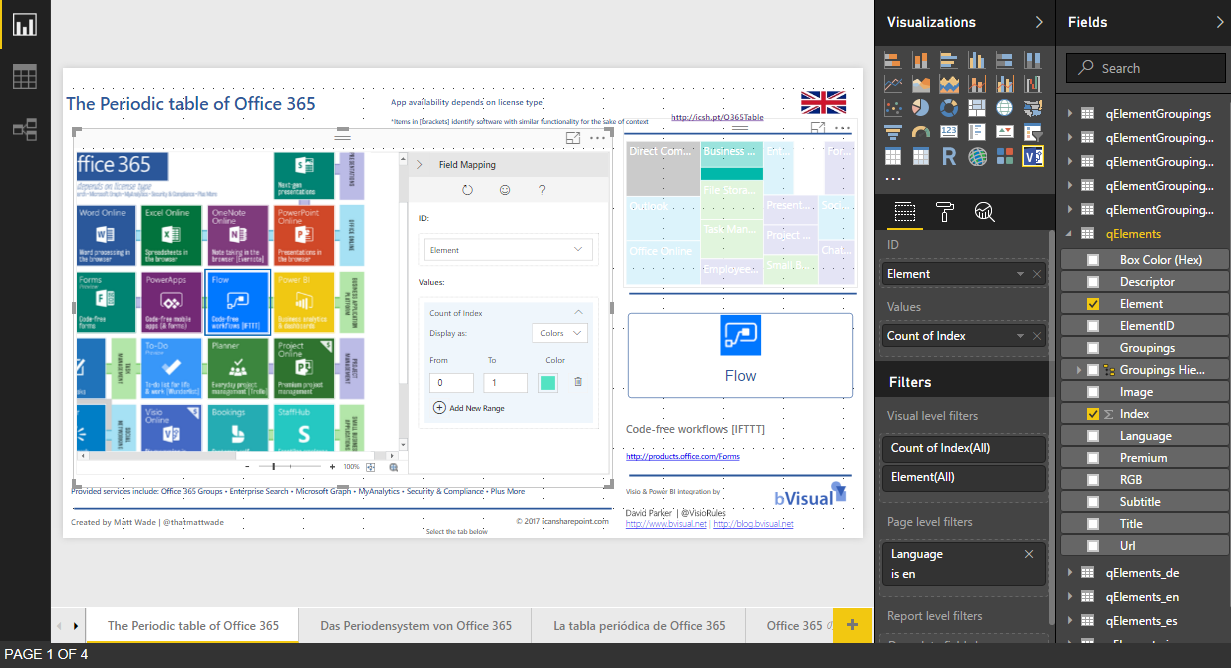
I went to a very interesting inaugural meeting of the South East UK Power BI Group last week. Whilst the presentation by Dr. Subramani Paramasivam was impressive for its ambition, it was the presentation by Andrew Fryer of Microsoft that particularly intrigued me. He introduced us to the world of Graph Databases, such as Neo4J and CosmosDB, but also demonstrated SQL Server 2017’s new Graph table types, called Node and Edge. He used the latter because solution because he could use example in Power BI using the Force-Directed visual. Well, this SQL Server feature was new to me, and so I was inspired to see if I could use my favourite tool, Visio, to input data into a graph database, and to selectively display parts.
This is something that I have often grappled with because, great as Visio is for diagramming, it is not the answer in all situations. It is brilliant at connecting shapes together, and adding data to each shape, including the connector, but it would not be fantastic at displaying all the millions of data points and relationships in any graph database worth its salt. However, what if another application, such as PowerBI, could be used to analyse and filter the information down to a more manageable scale, and then export the filtered data set to Visio where it can display the relationships, and be enhanced for inclusion in reports? Although I really like PowerBI, I do not think it generally provides an output that is report quality. Especially when reviewing the links between many nodes.
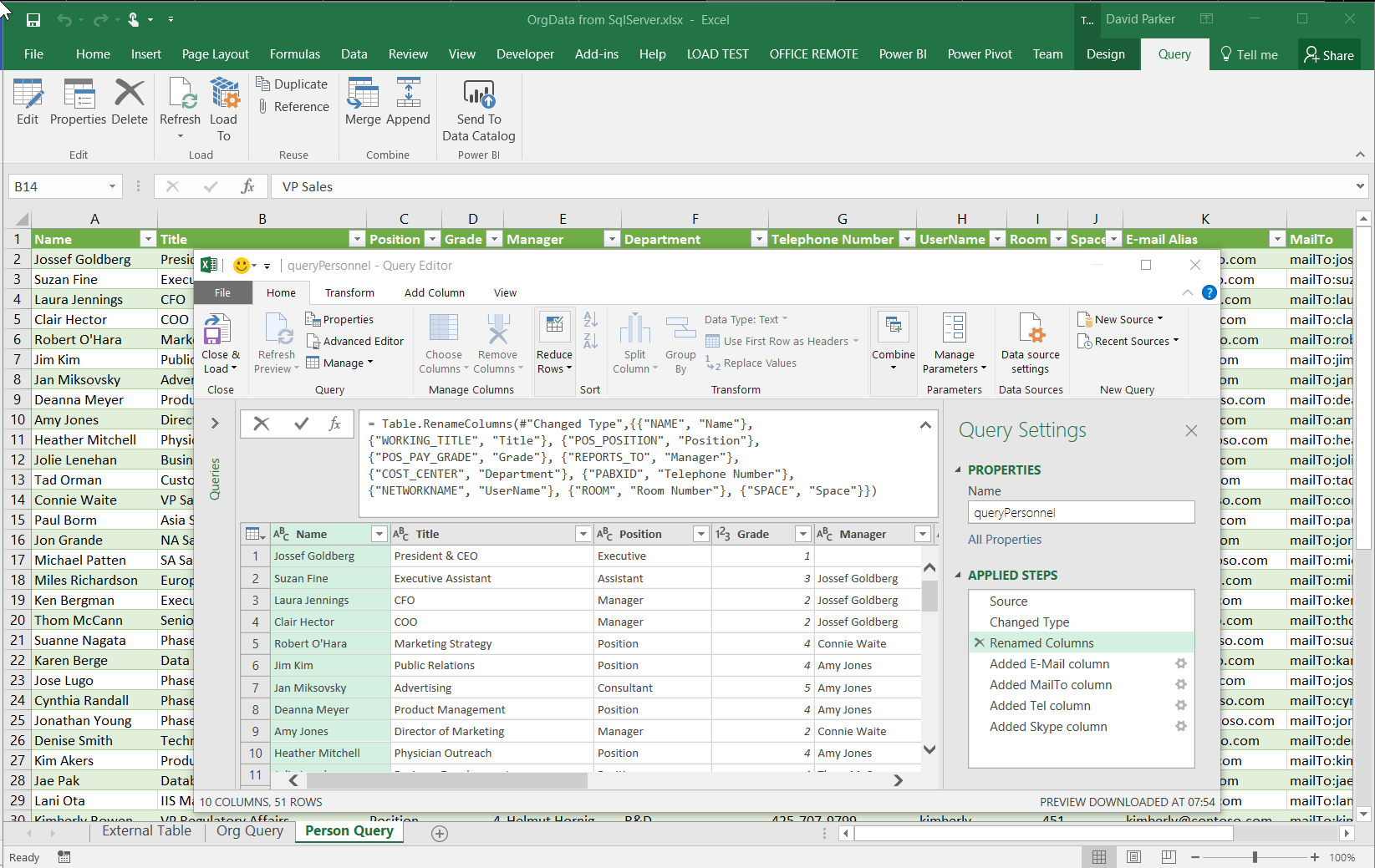
It is possible to insert data into SQL Server graph tables from csv files, but this is not always the most intuitive manner. Indeed, Andrew Fryer, whom I know to be a brilliant artist, resorts to sketching relationships freehand, and then creates tables or scripts from the diagram manually. So, what if you can use Visio to drag and drop nodes, and connect relationships between them, adding names and properties on the fly, as you go? Then, what if you could review your diagram, and then upload all of the nodes and edges to the database automatically? This process could be repeated on many pages, so that the data gets merged together in the graph database. The Visio pages can also be saved and remain available as a record of input, should any questions arise.
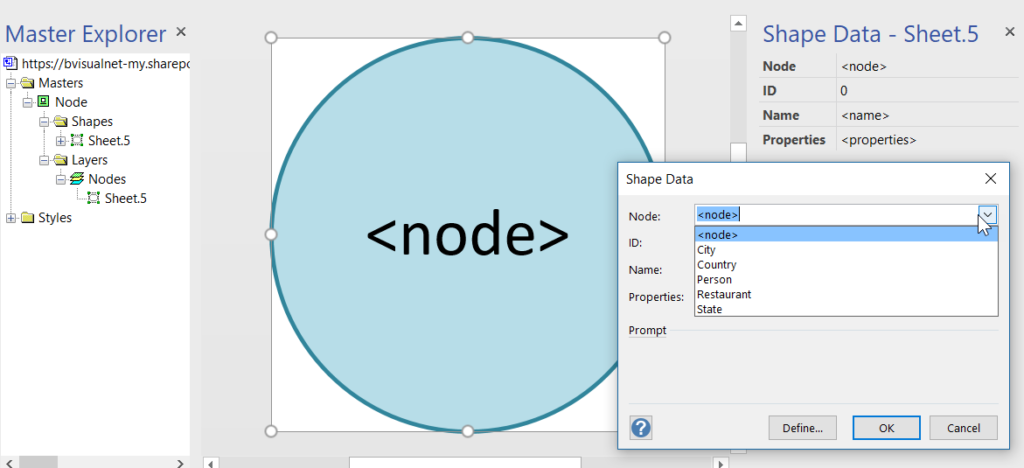
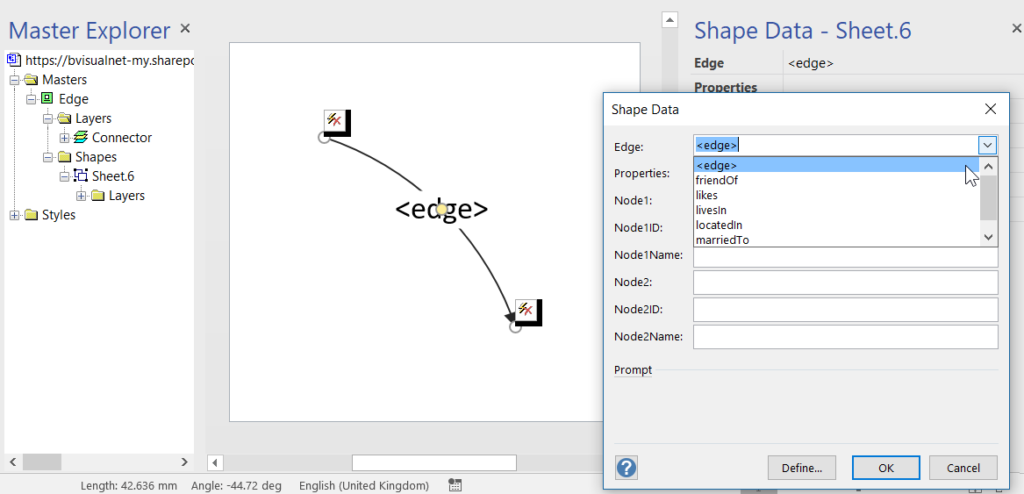
These new graph tables contain special column types that cannot be used directly by either PowerBI or Visio, so it is necessary to create views of the tables, thus effectively hiding them. I have a slight issue with the graphdemo database in the Microsoft article because it has extra columns on some Node and Edge tables. To me, this seems a little impure, and I think that the Node tables should only have an ID, Name and Properties column in addition to the Node columns, and the Edge tables should only have a Properties column in addition to the Edge columns. Ideally, the Properties columns in both tables should hold JSON data as text.
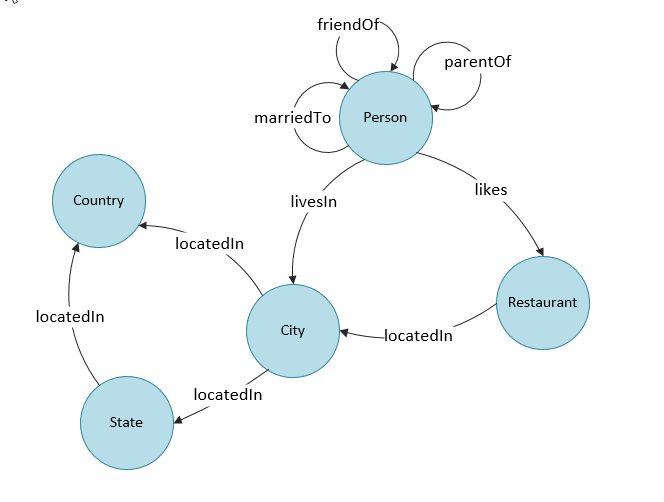
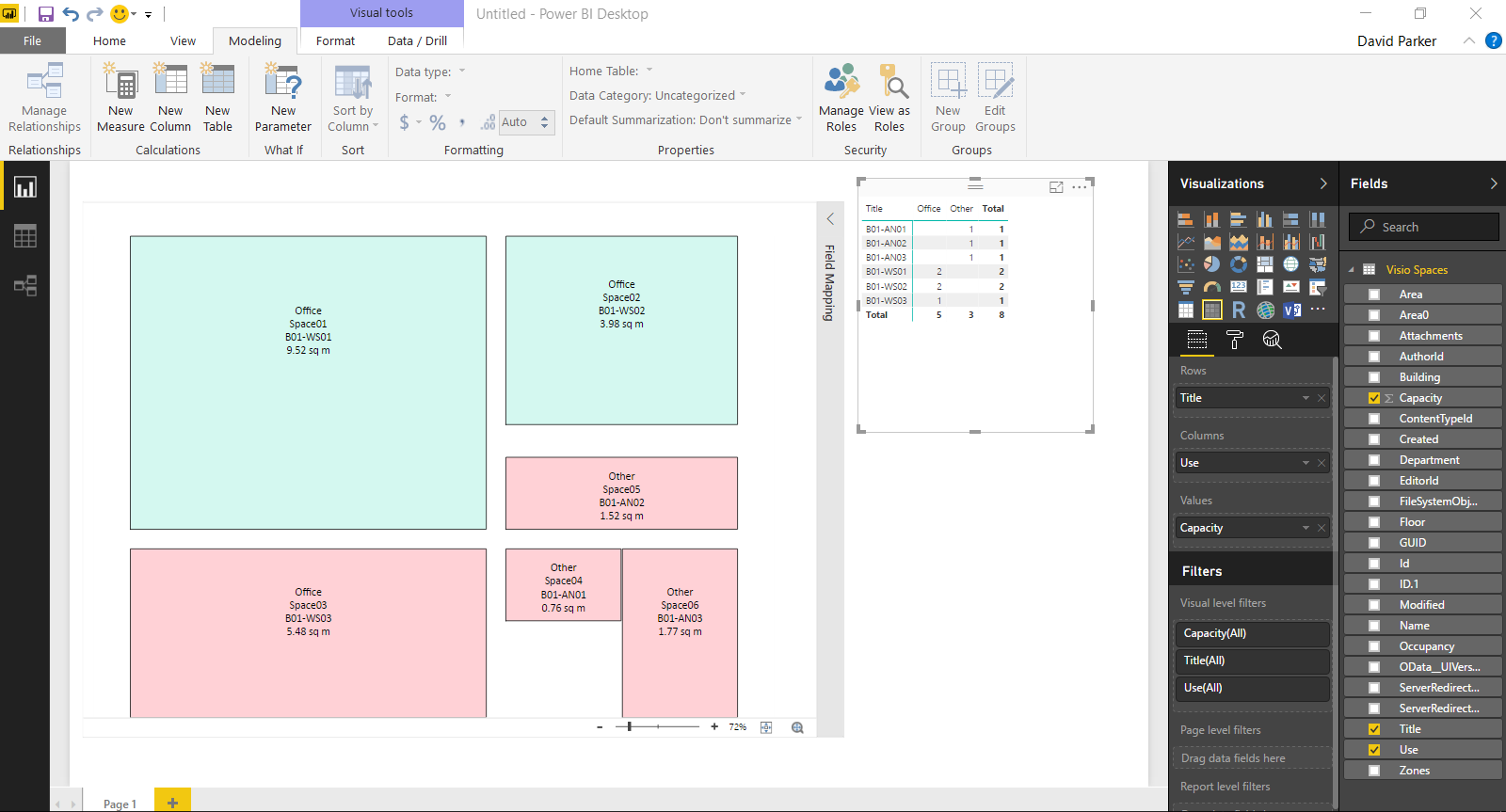
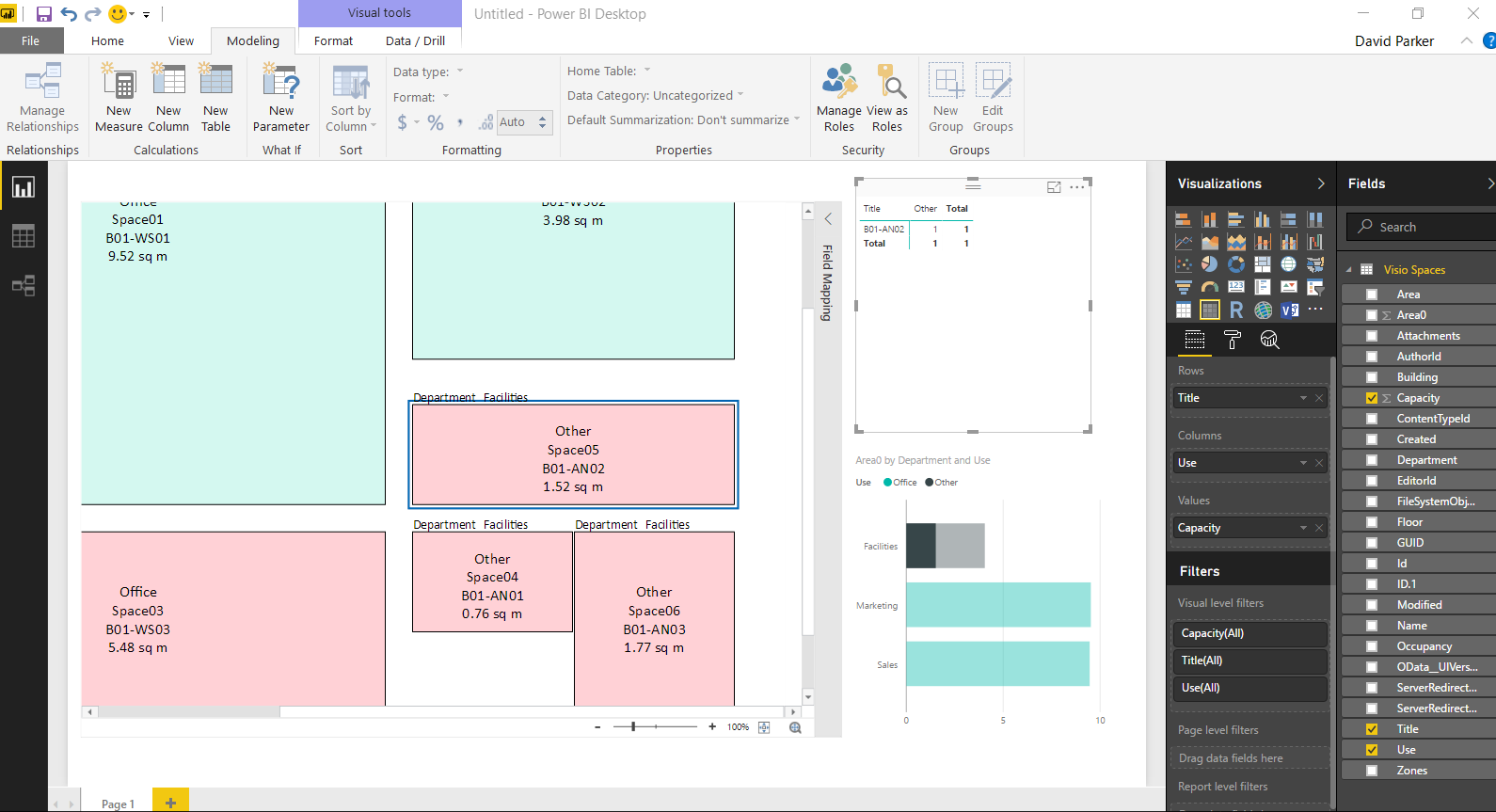
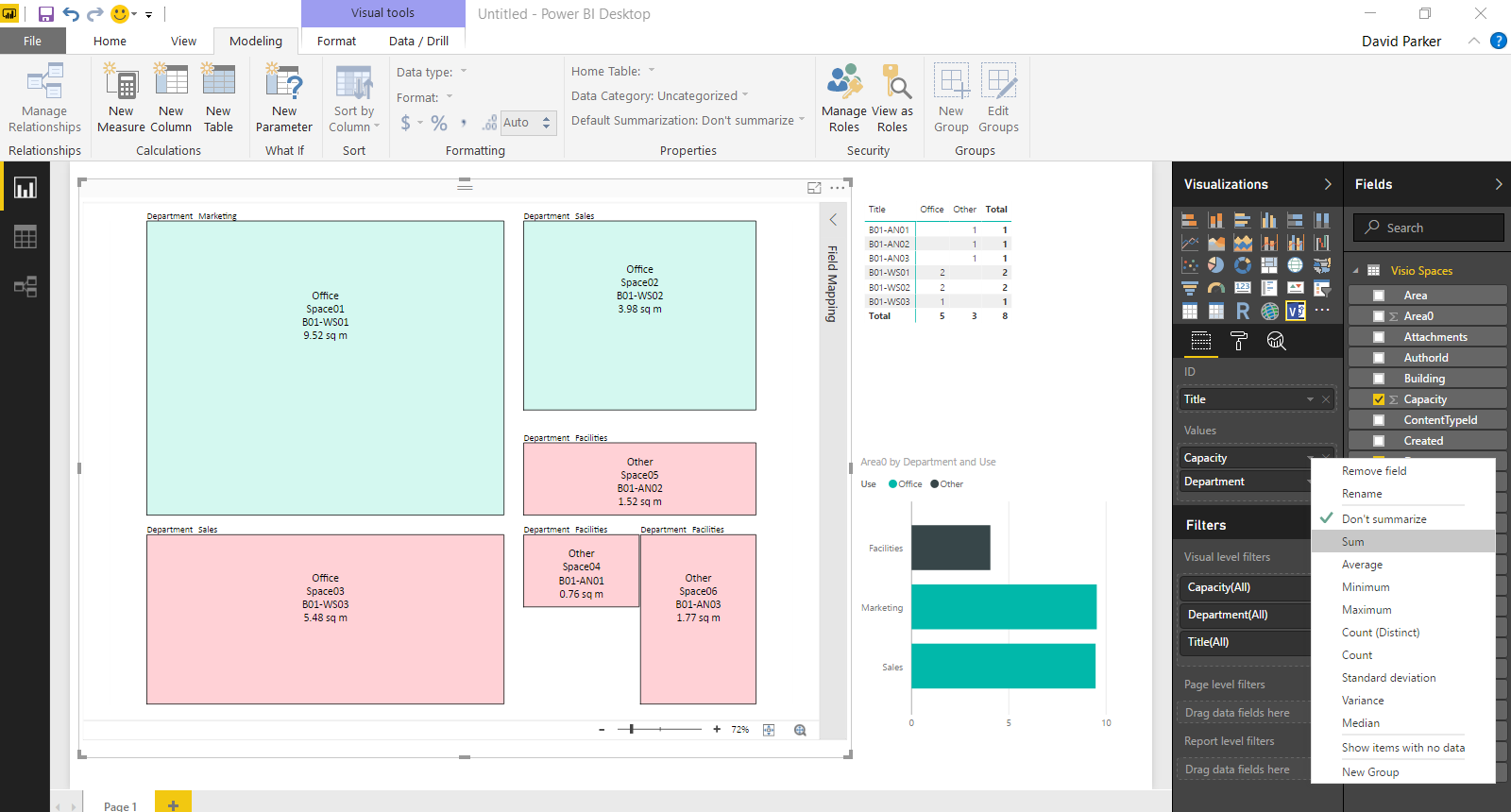
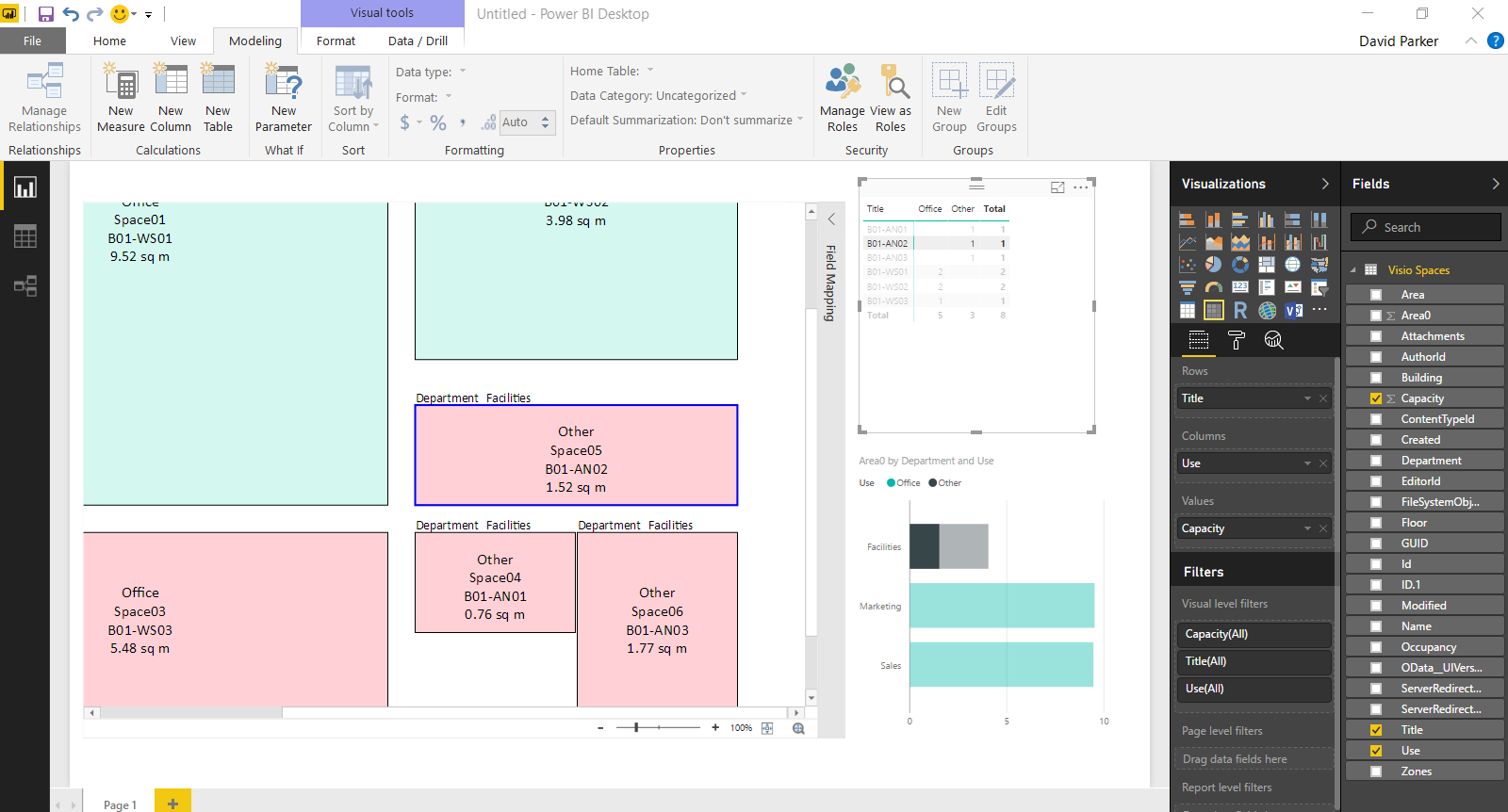
Anyway, I decided to create a proof of concept with just the basic Node and Edge attributes first. I also extended the sample database a little so I could have a bit more complexity. I decided to forget about using nice icons for now, and just keep it simple!